
Some theorists have posited that stories are all about problem-solving. And certainly – as we have seen – problems are at the very core of story. So by giving the audience a chance to vicariously experience protagonists dealing with problems, a story is in effect a sort of playground or simulation where we can experience what potential problems and solutions feel like – but without any real-life consequences.
An important consideration here is cause and effect. In real life, what we experience has so many causes that it is well-nigh impossible to accurately pinpoint them all. We constantly feel the effects, but it’s hard to pinpoint all the causes. Nonetheless, we really like to have explanations for what’s going on, it gives us a greater sense of control over our own lives. As a species, we seek agency, we’re always looking for what caused something to happen, for the why behind things being as they are. We find it very confusing when we don’t know the reason for the events we live through, and we build elaborate mental constructs to explain to ourselves the world as we perceive it. In this context, we sometimes speak of “narratives”.
In stories, every scene must be the result of a preceding plot event. As we have said before, in between each plot event of a narrative you should be able to place the words not “and then”, but “because of that …”. (more…)

 Here at Beemgee, we’re into the thought behind the writing of stories more than the writing itself. So we’re all the more pleased that Writer.com approached us to talk about character development. While their speciality is AI-assisted text generation for companies, in their guest post, they have some good general advice on creating fictional characters. Thanks to Nicholas Rubright for this article. Nickolas is a digital marketing specialist and expert at Writer. In his free time, he enjoys playing guitar, writing music, and building cool things on the internet.
Here at Beemgee, we’re into the thought behind the writing of stories more than the writing itself. So we’re all the more pleased that Writer.com approached us to talk about character development. While their speciality is AI-assisted text generation for companies, in their guest post, they have some good general advice on creating fictional characters. Thanks to Nicholas Rubright for this article. Nickolas is a digital marketing specialist and expert at Writer. In his free time, he enjoys playing guitar, writing music, and building cool things on the internet.
Writing characters with whom readers can identify and empathize should be the goal of every writer, but it’s not a simple task.
To fully grasp a character’s motivations, desires, and anxieties, writers must dive deep into the character’s psyche. Character flaws and strengths work together to build a solid character.
But what is the most effective way to develop a character? And how can you establish a connection between your character’s dramatic decisions and the story itself?
Your characters are the heart and soul of your story. Thus, before you can write a single word, you must first understand your characters.
When it comes to character creation, you have several choices to make, and each choice affects the story in its own way. You must, however, choose what works best for your character.
While an unexpected detail can make the character more interesting, if it isn’t chosen carefully it can damage the character’s believability and ruin your reader’s immersion in your story.
Here are some guidelines and tricks to help you successfully create mouldable character templates for your story.
So, let’s dive in! (more…)

Nothing should be more important to an author than how their story makes the audience feel.
As an author, consider carefully the emotional journey of the reader or viewer as they progress through your narrative.
The audience experiences a sequence of emotions when engaged in a narrative. So narrative structure is a vital aspect of storytelling. The story should be touching the audience emotionally during every scene. Furthermore, each new scene should evoke a new feeling in order to remain fresh and surprising.
The author’s job is to make the audience feel empathy with the characters quickly, so that an emotional response to the characters’ situation is possible. Only this can lead to physical reactions like accelerated heartbeat when the story gets exciting. We have to care.
This “capturing” of the audience, making the reader or viewer rapt and enthralled, requires authors to create events that will show who the characters are and how they react to the problems they must face. The audience is more likely to feel with the characters as the plot unfolds when the characters’ reactions to events reveal something about who they really are – and how they might be similar to us.
One Journey to Spellbind Them All
Here we present a loose pattern that we think probably fits for any type of story, whatever genre or medium, however “literary” or “commercial”. It’s not prescriptive, just a rough checklist of the stages in the emotional journey the audience tacitly expects when they let themselves in on a story. The emotions are in more or less the order they might be evoked by any narrative.
Curiosity
(more…)
Stories tend to show characters getting together.

Stories don’t get going until there are at least two characters.
That’s because the characters in themselves are not really what interests the audience. What the audience likes to experience is relationships.
At a fundamental level, there are only these three ways that people – or characters within a story – can interact with each other:
- they can cooperate
- they might oppose each other
- or they may get together
It is the complexities of these types of relationship that authors present to their audiences.
At least two of the three types of relationships are likely to be depicted in any story, cooperation and conflict. To make the story feel complete, authors especially of popular stories such as Hollywood movies often include the third type in the form of a love interest. (more…)
Reflections on dialectically guided writing, or: Can dialectics help us tell better stories?
 Guest post by Richard Sorg.
Guest post by Richard Sorg.
Prof. Dr. phil. Richard Sorg, born in 1940, is an expert in dialectics. What is that, and what does it have to do with my novel? Well, “All great, moving and convincing stories are inconceivable without the central significance of the contradictions and conflicts that represent the driving energy of movement and development.” This puts us in the middle of dialectics. And of storytelling.
After studying theology, sociology, political science and philosophy in Tübingen, West Berlin, Zurich and Marburg, Richard Sorg taught sociology in Wiesbaden and Hamburg. His book “Dialectical Thinking” was recently published by PapyRossa Verlag. (Photo: Torsten Kollmer)
Ideas that contain a potential for conflict.
Sometimes there is a single but central chord at the beginning of a piece of music, even an entire opera, which is then gradually unfolded. Its inherent aspects, harmonies and dissonances emerge from the chosen, sometimes inconspicuous beginning, undergoing a dramatic, conflictual development, so that a whole, complex story emerges at the end of the path of this simple chord after its unfolding. This is the case, for example, with the so-called Tristan chord at the beginning of Richard Wagner’s opera “Tristan und Isolde”, a leitmotif chord that ends with an irritating dissonance.
The beginning of a story is sometimes an idea, an idea which you may not know how to develop. But some such ideas or beginnings carry a potential within them that is capable of unfolding and which holds unimagined development possibilities. ‘Candidates’ for viable beginnings – comparable to the dissonant Tristan chord mentioned above – are those that contain a potential for conflict or contradiction within. But it can also be a calm with which the matter is opened up, a calm that may then prove to be deceptive. We also find something similar in some dramas, for example with Bertolt Brecht.
And with that, we are already in the middle of dialectics. (more…)

Conflict is the Lifeblood of Story.
In real life, conflict is something we generally want to avoid. Stories, on the other hand, require conflict. This discrepancy is an indicator of the underlying purpose of stories as a kind of training ground, a place where we learn to deal with conflict without having to suffer real-life consequences.
In this post we will look at:
- An Analogy
- Archetypal conflict in stories
- Conflict between characters
- Conflict within a character
- The central conflict
Along with language (in some form or other, be it as text or as the language of a medium, such as film) and meaning (intended by the author or understood by the recipient), characters and plot form the constituent parts of story. It is impossible to create a story that does not include these four components – even if the characters are one-dimensional and the plot has no structure. However, it is formally possible to compose a story with no conflict.
It just won’t be very interesting.
In terms of narrative, conflict is presented as a series of confrontations of increasing intensity. If there are no confrontations – no battles of wits or fists, no crossing of swords or sparring with words – there is little to hold the audience’ attention. To create confrontations, there must be at least a of conflict of interest between the characters.
Conflict does not occur at particular points in a story. It permeates the whole of it. It expresses the values transported by the story’s theme. It creates at least two options of choice, both of which must appear to some extent reasonable and justifiable to the protagonist, particularly at the moment of crisis.
(more…)
A plot arises out of the actions and interactions of the characters.
On the whole, you need at least two characters to create a plot. Add even more characters to the mix, and you’ll have possibilities for more than one plot.
Most stories consist of more than one plot. Each such plot is a self-contained storyline.
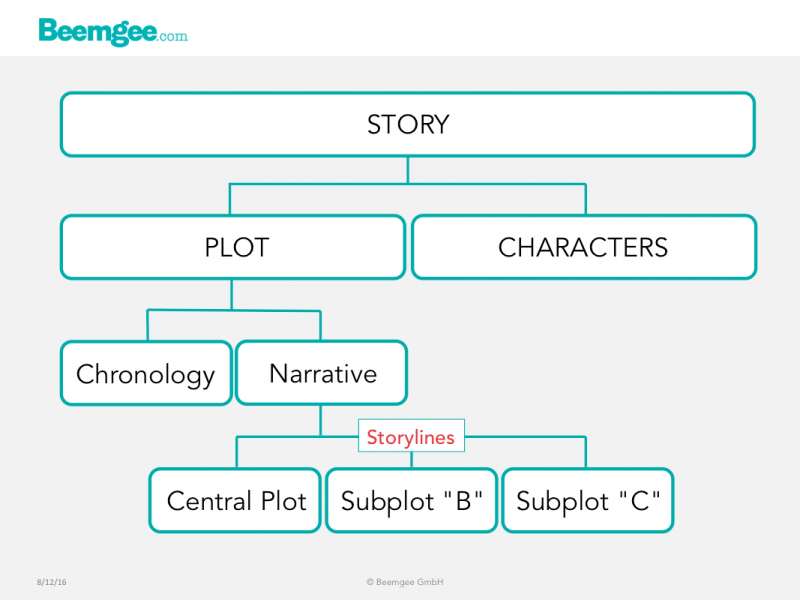
The Central Plot
Often there is a central plot and at least one subplot. The central plot is usually the one that arcs across the entire narrative, from the onset of the external problem (the “inciting incident” for one character) to its resolution. This is the plot that is at the(more…)
In stories, the characters’ emotions are ultimately the sources of their actions, because motivations are ultimately based on emotions.
Determining the emotional core of a character in a story may lead to a clearer understanding of that character’s behaviour, i.e. their actions.
What we’re getting at here is essentially a premise for creating a story. We have noted that if you plonk a group of contrasting characters in a room – or story-world –, then a plot can emerge out of the arising conflicts of interest. If you’re designing a story, one approach is to create the contrasts between the characters (their essential differences of character) by giving each character a core trait or emotion. One character may be frivolous, another penny-pinching. One may be fearful, another cheeky.
You might object: Isn’t that a bit one-dimensional? Aren’t characters with just one core emotion flat?
Not necessarily. Focusing on one core emotion is not a cheap trick. It is as old as storytelling.
Classical Storytelling
Ancient(more…)

A character in a story has values and passions. In short, an emotional stance. It’s this bundle of feelings that make the character a character.
By emotional stance we mean a value-set. This is particularly important when one considers that often stories show value-sets in conflict. The protagonist and in particular the protagonist’s journey to recognition and change may represent certain values. These will be in direct contrast to the antagonist’s values. The theme of the story presents one value-set as preferable over the other.
In many stories, the protagonist starts out with a value-set that is warped or flawed. Their real need is to become aware that their value-set is harmful or negative, probably ultimately selfish, and find a way to gain new values that are more social, cooperative and selfless. For the purpose of such a story, the values are initially expressed in the internal problem and by the end have gone through a change.
Values do not emerge in a vacuum, they are instilled by environment or culture. Stories exhibit cause and effect, and the values of each of the characters are no exception. The audience looks for the causes of a character’s emotional stance. By the very nature of emotions and values, their causes can be hard to pinpoint – while at the same time being somewhat obvious. In stories, at least.
Furthermore, values are emotional and therefore exist before they are articulated. A character becomes conscious of a value-set in the form of a system of beliefs. The beliefs are articulated by the character as convictions, and are determined by inner values. In some cases, the stated beliefs may actually be in conflict with the character’s deeper values, of which the character may not be entirely aware. Values tend to feel right to the individual, though they may actually be wrong for the larger community or society.
A character’s values have to be plausible to the audience, which may be achieved for instance giving the characters appropriate social backgrounds or origins and making these explicit. In many stories, a character’s upbringing or their origin is named or described in order to explain their emotional stance.
Alternatively, values may be caused by certain specific events in the history or background of a character, conveyed as backstory in the narrative. A particular circumstance, possibly a trauma, leads the character to feel a certain way about life and the world.
Character Values in Historical Stories
In historical stories the time-setting is particularly challenging in terms of the emotional stance of the characters. Much popular historical fiction may justly be termed anachronistic in that it has characters – especially female protagonists! – exhibiting values and beliefs which do not fit into the time. For example: In the Middle Ages, the advent of humanism had not occurred yet. There had been no Renaissance, no Descartes, no Kant, no French Revolution and no American Constitution. Where is a character in the Middle Ages supposed to get ideas, values and convictions from that today we take for granted? Ideas about inalienable rights such as liberty and equality or concepts such as individualism. People in the past had different values and belief systems from people today, and it is almost impossible to put ourselves in their shoes. Historical fiction that does not at least implicitly deal with this challenging issue is more likely to be clichéd and trivial.
Which does not mean that trivial historical stories can’t be wildly entertaining with strong emotional impact. After all, modern stories address the audience of today. It means simply that an author usually has some sort of attitude to the issue.
Photo by Wonderlane on Unsplash
Related function in the Beemgee story development tool:
Character Developer
Already using the author tool? If not, try it here:

Stories need characters. What the characters do creates the plot.
With a well-rounded cast of characters, the plot will almost take care of itself. A story gets energy from the dynamic that occurs between the all the characters in it. The interaction between the characters is fueled by contrast, motivations, and conflict. Put a bunch of characters in a room – i.e. on a stage, between the covers of a book, between the first and last shots of a movie – and the plot is likely to emerge on its own. As long as there are contrasts between the characters and their motivations, conflict will arise.
So how does an author cast the characters that bring the story to life?
First of all, one character is rarely enough. Almost all stories need several characters. Even Robinson Crusoe couldn’t hold out alone. It’s the interplay between characters that creates interest. For interplay, read conflict.
Conflict in storytelling does not mean fights and battles. It means a conflict of interests.
Characters become characters because they have interests. Their interests make them do what they do, and this doing is what drives the plot.
What does that mean?
It means characters are motivated. They(more…)



 Here at Beemgee, we’re into the thought behind the writing of stories more than the writing itself. So we’re all the more pleased that
Here at Beemgee, we’re into the thought behind the writing of stories more than the writing itself. So we’re all the more pleased that 

 Guest post by Richard Sorg.
Guest post by Richard Sorg.



